Ingestion Tokens
Create and manage tokens for sending telemetry data to Last9, including RUM and Prometheus metrics.
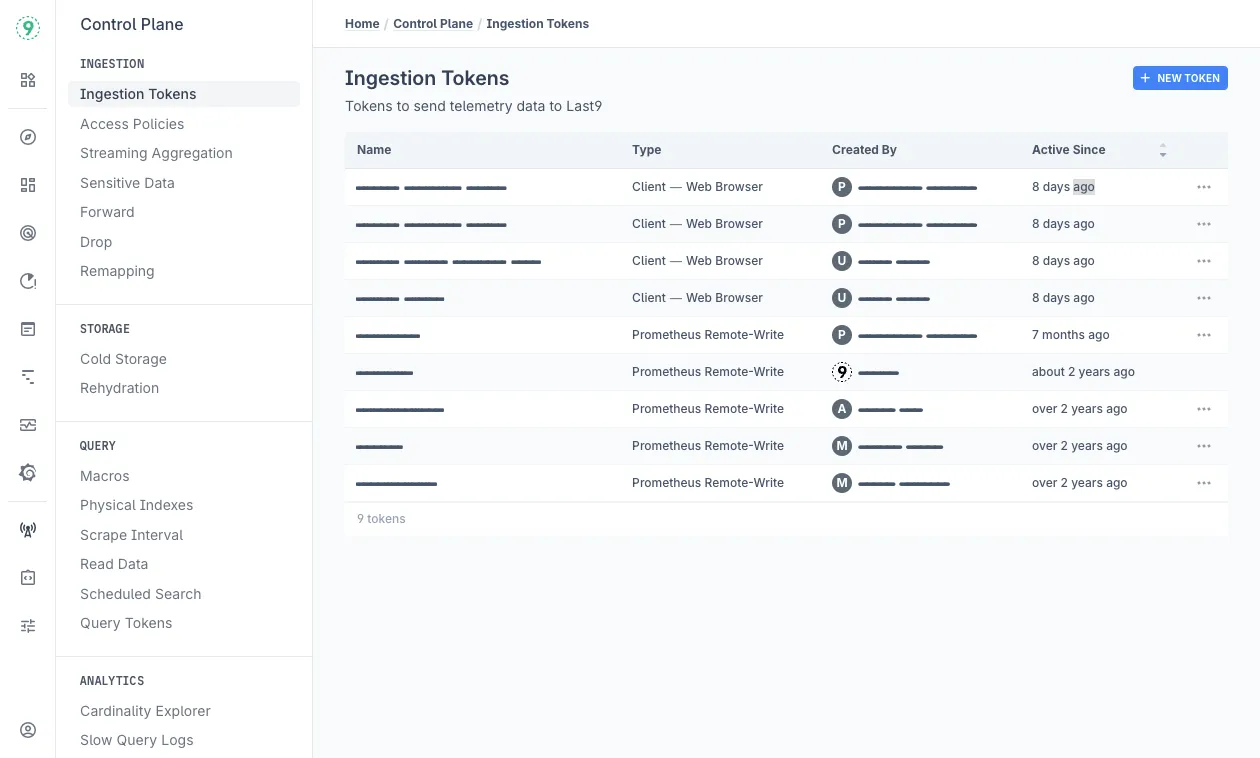
Ingestion Tokens authenticate your applications and services when sending telemetry data to Last9. These tokens control what data can be sent and from which origins, ensuring secure data collection.
Creating Ingestion Tokens
-
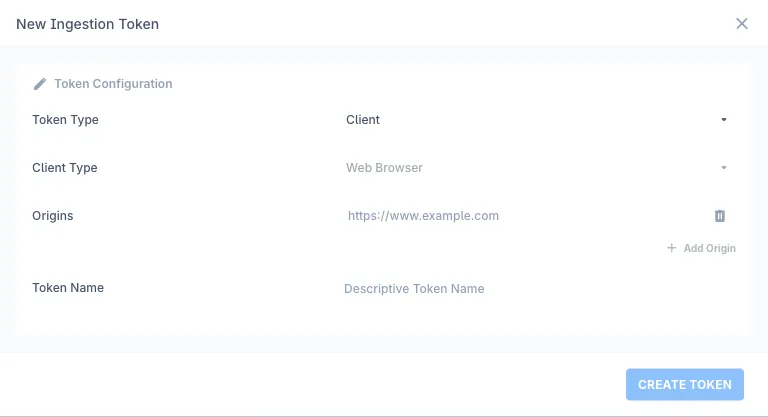
Select Token Type:
- Client: For client-based data collection (eg: RUM)
- Prometheus Remote-Write: For server-side Prometheus-compatible metrics
-
Configure Client Type (if Client selected):
- Web Browser: Default and currently available option for web applications
- Mobile: Coming soon for mobile app monitoring
-
Set Origins (for Client tokens):
- Add the domains from which your application will send data
- Example:
https://www.example.com - Multiple origins can be added for multi-domain applications
- Wildcard subdomains are supported using
*.prefix (e.g.,https://*.example.com)
✅ Correct Origins:https://app.example.comhttps://www.example.comhttp://localhost:3000https://*.example.com (matches any single subdomain)https://*.apps.example.com (matches subdomains of apps.example.com)https://app.*.example.com (matches app.{any}.example.com)❌ Incorrect Origins:example.com (missing protocol)app.example.com (missing protocol)https://example.* (TLD must be explicit, e.g., .com, .io)Wildcard Origins
Wildcard origins allow you to match multiple subdomains with a single entry. This is useful when:
- Your application serves multiple customer subdomains (e.g.,
customer1.example.com,customer2.example.com) - You have dynamic environments that create subdomains on the fly
- You want to simplify token management across many subdomains
Wildcard Rules:
Pattern Matches Does Not Match https://*.example.comhttps://app.example.com,https://www.example.comhttps://example.com,https://sub.app.example.comhttps://*.apps.example.comhttps://prod.apps.example.com,https://dev.apps.example.comhttps://apps.example.comhttps://app.*.example.comhttps://app.staging.example.com,https://app.prod.example.comhttps://app.example.com -
Name Your Token:
- Use a descriptive name to identify the token’s purpose
- Example: “Production RUM Token” or “Staging Web Monitoring”
-
Click CREATE TOKEN to generate your token
Client Token Security
Is the Client Token Safe to Expose?
Yes. Client tokens are specifically designed to be visible in your frontend code and are safe to include in your application bundle.
Why Client Tokens Are Safe
- Write-Only Permissions: Client tokens can only send telemetry data to Last9. They cannot read, query, or access any data from your account.
- CORS-Restricted: Tokens are restricted to the origins (domains) you configure above, preventing unauthorized websites from using your token.
- No Account Access: Client tokens cannot access your Last9 account settings, billing information, or any other sensitive data.
- Designed for Public Use: This security model is standard across the industry for frontend monitoring.
Why Not Use API Keys?
API keys have full read/write access to your entire Last9 account and should never be exposed in frontend code. Client tokens exist specifically to provide a safe way to send telemetry from browsers.
Security Best Practices
While client tokens are safe to expose, follow these practices to minimize abuse:
-
Rotate Tokens Periodically: Rotate your client tokens every 90 days as a preventive measure.
-
Restrict CORS Origins: Configure allowed origins (as shown above) to only accept data from your domains.
-
Use Different Tokens Per Environment: Use separate tokens for development, staging, and production.
-
Monitor Usage: Regularly review your usage dashboard to detect unusual patterns or potential abuse.
Handling CI/CD Security Scanners
Your CI/CD pipeline security scanners may flag client tokens as secrets. This is a false positive. To resolve:
GitGuardian / GitHub Secret Scanning
Add an exception for client tokens:
# .gitguardian.ymlpaths-ignore: - "**/*.html" - "**/rum-config.js"
allow-patterns: - "clientToken.*" - "L9RUM\\.init"Inline Comment Exception
Add security scanner directives:
// gitguardian:ignore - Public client token with write-only permissions// nosemgrep: generic.secrets.security.detected-generic-secretconst CLIENT_TOKEN = "your-token-here";Troubleshooting
Please get in touch with us on Discord or Email if you have any questions.