Effective control of operational expenses plays a crucial role in the deployment and administration of Kubernetes. While Kubernetes empowers users with enhanced control over deployments, it requires a deep understanding and effective management of associated costs. OpenCost, tailor-made for Kubernetes cost monitoring, paired with Last9, presents a holistic solution to address this challenge.
In this blog we will learn how to integrate existing OpenCost setup with Levitate for monitoring Kubernetes costs.
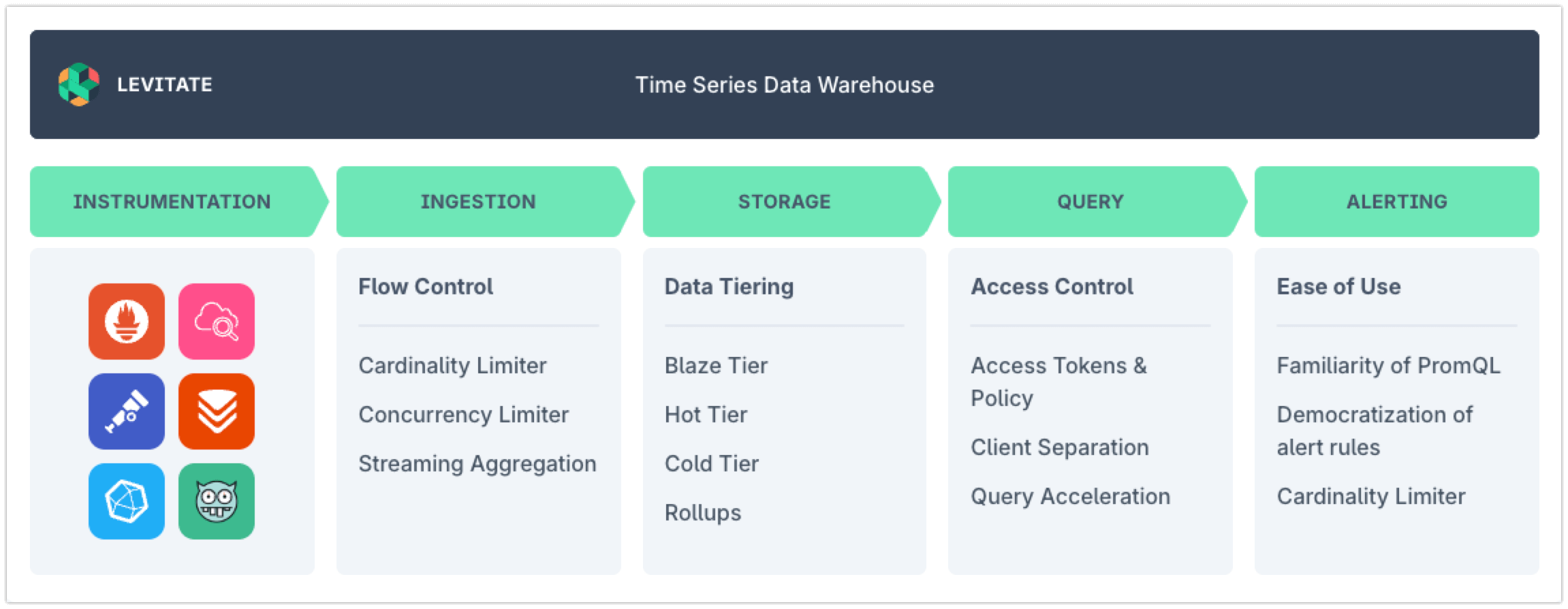
What is Levitate?
Levitate is a managed time series metrics and events warehouse. It is compatible with Prometheus and OpenTelemetry and provides better performance and workflows to tame high cardinality.
What is OpenCost?
OpenCost is a CNCF-backed open-source cost monitoring tool for cloud-native environments, built to offer a complete view of Kubernetes cluster costs across various cloud providers, regions, and on-premises installations. It enables real-time monitoring of Kubernetes cluster costs, providing a detailed breakdown for each resource.
OpenCost relies on the metrics emitted by node-exporter and kube-state-metrics (KSM). It queries the underlying TSDB storage for these metrics. It also ships with a web UI for visualization and a Grafana dashboard.
OpenCost also has built-in integrations with cloud providers using their APIs to retrieve billing information.
OpenCost Installation
OpenCost can be installed using Helm. It assumes an existing Prometheus Operator installation. You can follow along with the documentation and carry out the installation.
Connecting OpenCost to Levitate
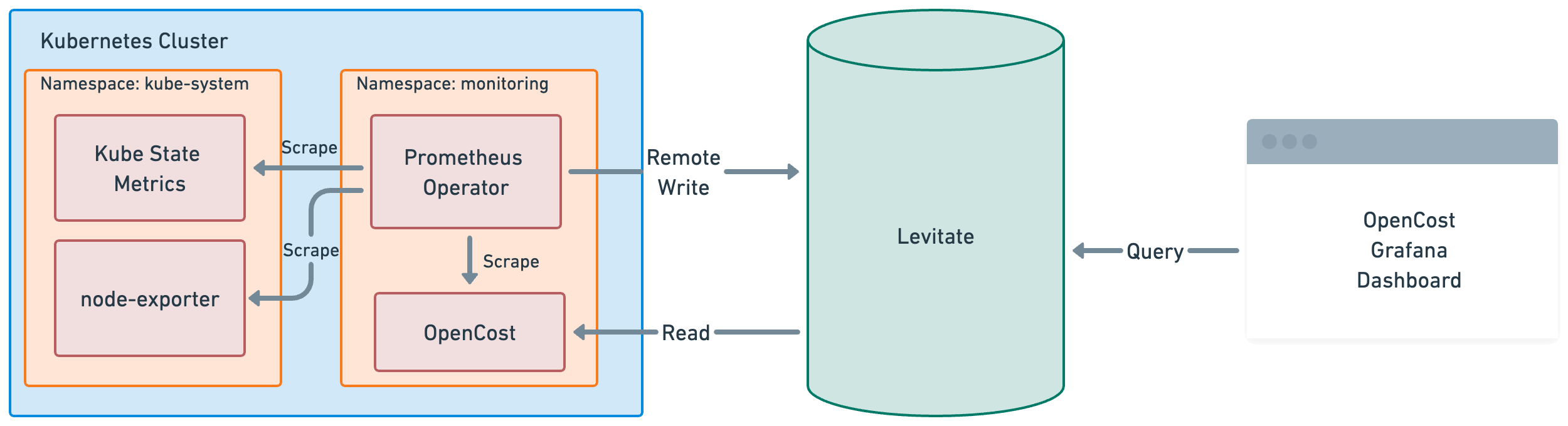
Integrating OpenCost with Levitate is super easy as it requires a minimal configuration change to be deployed. OpenCost assumes that the required metrics to be queried are stored in a TSDB like Levitate. It involves following steps.
- Configure Prometheus Operator to remote write Kubernetes metrics such as
kube-state-metricsandnode-exporterto Levitate. - Additionally, Prometheus Operator can be configured to scrape metrics that OpenCost emits and send them to Levitate.
- Read metrics from Levitate needed for OpenCost. Obtain the OpenCost Helm Chart
values.yaml. If you have customized your Helm Chart values, use that instead of the default file. - Update OpenCost Helm Chart
values.yamlwith Levitate Read Credentials. Obtain Read Credentials following this guide. - Replace the default config with the below-modified config. Update placeholders with proper authentication credentials as obtained earlier.
prometheus:
# -- Secret name that contains credentials for Prometheus
secret_name: ~
# -- Prometheus Basic auth username
username: "<levitate_username>"
# -- Key in the secret that references the username
username_key: DB_BASIC_AUTH_USERNAME
# -- Prometheus Basic auth password
password: "<levitate_password>"
# -- Key in the secret that references the password
password_key: DB_BASIC_AUTH_PW
# -- Prometheus Bearer token
bearer_token: ""
bearer_token_key: DB_BEARER_TOKEN
external:
# -- Use external Prometheus (eg. Levitate)
enabled: true
# -- External Prometheus url
url: "<levitate_read_url>"
internal:
# -- Use in-cluster Prometheus
enabled: false
# -- Service name of in-cluster Prometheus
serviceName: prometheus-server
# -- Namespace of in-cluster Prometheus
namespaceName: prometheus-system
# -- Service port of in-cluster Prometheus
port: 80Ensure that Prometheus is an external data sourceenabledis set totrueand internalenabledis set tofalse.
- Thats it! Clean and simple 👌 Deploy Helm Chart with these updated configs
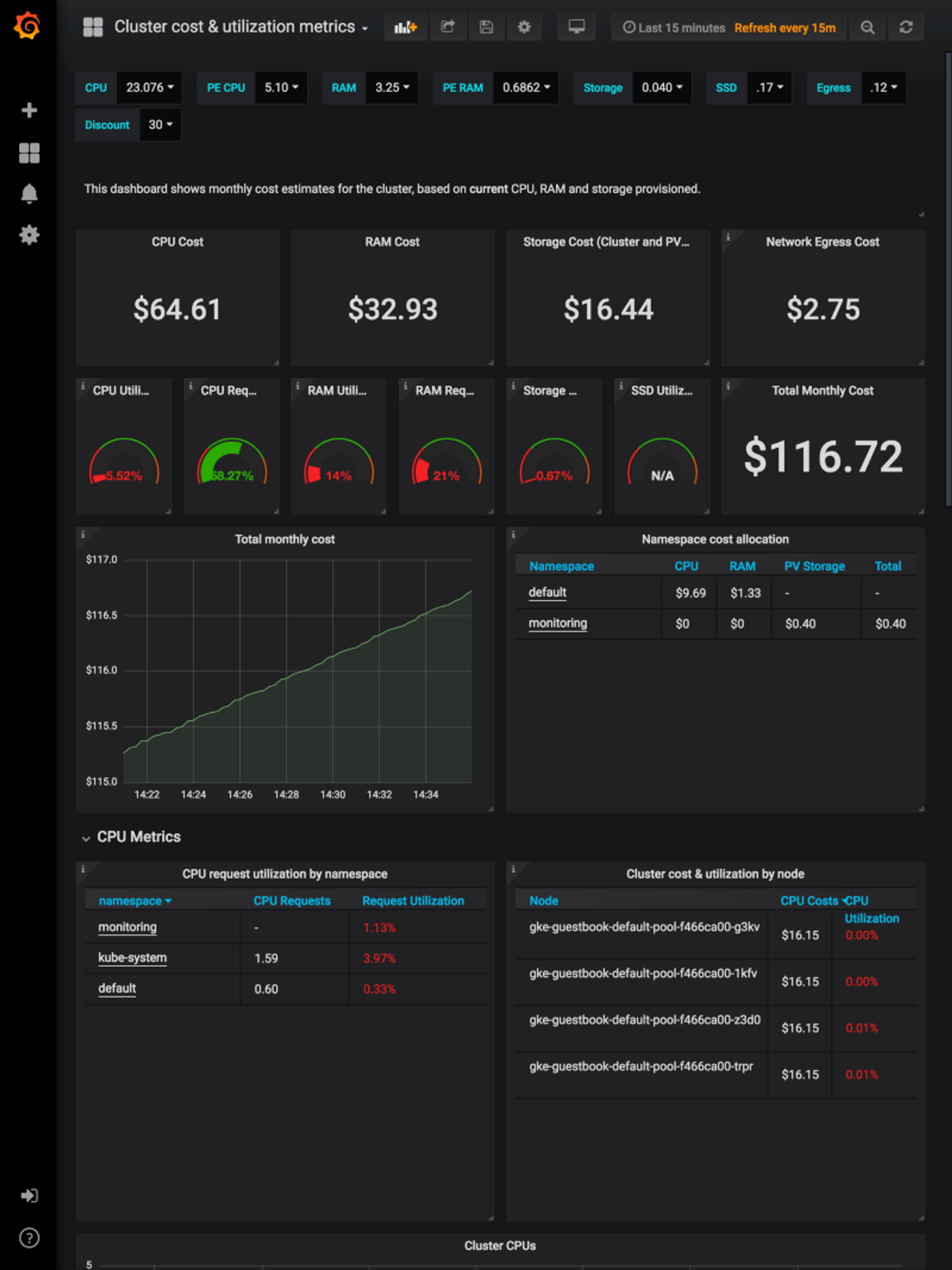
helm upgrade opencost opencost/opencost -f ./values.yaml --kubeconfig=/path/to/kubeconfigOpenCost Grafana Dashboard
Import this dashboard is provided by OpenCost here.
Conclusion
In summary, effective Kubernetes management requires careful monitoring of operational costs. OpenCost, offering a comprehensive view of Kubernetes costs across diverse platforms, coupled with Levitate's efficient time-series data storage and powerful alerting workflows, creates a powerful cost monitoring system. Together, they enable real-time tracking, detailed cost breakdowns, and insightful visualizations, ensuring optimal financial efficiency in Kubernetes deployments.