Logging is essential for system observability, error handling, and troubleshooting. While traditional logging is useful, it often falls short when handling large volumes of data and providing the intricate context needed to understand issues.
structlog—a powerful Python library designed to take logging to the next level by making it structured, readable, and machine-friendly. This guide explores how structlog can enhance your logging strategy, improve system observability, and ultimately help you build more reliable software.

What is Structlog and Why Should You Use It?
structlog is a Python library that helps you build structured logs—logs containing key-value pairs. This makes them more informative and easier to analyze. Unlike traditional text-based logs, structured logs capture context more effectively, aiding debugging, monitoring, and performance analysis.
With structlog, you can integrate structured logging into your existing Python applications, providing clear and concise insights into the inner workings of your code.
The Core Advantages of Using Structlog
Structured Logs for Improved Readability and Analysis
Traditional logging outputs plain text, which can be difficult to parse in large-scale systems or microservices. Structured logging formats logs as key-value pairs, making filtering, querying, and analysis much easier.
Critical details such as error codes, timestamps, and request IDs become readily accessible, simplifying debugging and monitoring.
Context Preservation for More Informative Logs
structlog excels at maintaining context throughout log entries. By attaching metadata such as user information, session IDs, or transaction statuses, you gain deeper insights into your application’s state when issues arise.
This added context simplifies tracing the root cause of problems.

Customizable Pipelines for Log Processing
structlog provides flexible pipelines to format, process, and store logs. Whether you log to a file, cloud service, or monitoring tool, structlog lets you tailor outputs to meet specific needs.
Consistent formatting ensures compatibility with your team’s standards and observability tools.
Getting Started with Structlog
Installing Structlog
pip install structlogBasic Configuration
Configure structlog alongside Python’s built-in logging module:
import structlog
import logging
logging.basicConfig(format="%(message)s", level=logging.INFO)
log = structlog.get_logger()
log.info("Application started", app="my_app", user="admin")This example demonstrates structured metadata in a log entry, making logs more insightful.

Key Concepts in Structlog
Processors
Processors are functions that transform log entries. For instance, you can add a timestamp or redact sensitive information:
import structlog
import datetime
def add_timestamp(_, __, event_dict):
event_dict["timestamp"] = datetime.datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
return event_dict
log = structlog.get_logger().bind(processors=[add_timestamp])
log.info("Processed log with timestamp")Loggers and Bindings
Create loggers bound to consistent metadata, such as session or user IDs:
log = structlog.get_logger().bind(session_id="12345", user="john_doe")
log.info("User action logged")Rendering and Output
Customize log rendering. structlog outputs JSON-like formats by default, but you can switch to plain text or log to external services like Datadog or Elasticsearch.
Structlog vs Traditional Logging
Clarity and Structure
With structlog, enriched key-value logs improve readability and filterability.
Scalability
Structured logs scale better with growing systems, enhancing traceability.
Tool Integration
structlog integrates easily with observability tools like Prometheus, Datadog, and ELK stack.

Advanced Structlog Features
Asynchronous Logging
Avoid performance bottlenecks with asynchronous logging, ensuring logs don’t block application logic.
Integration with External Libraries
Combine structlog with libraries like loguru for advanced features, ideal for large-scale applications.
Structlog Use Cases
Microservices Architectures
Attach unique request IDs to logs, making it easier to trace logs across distributed services.
Real-time Monitoring
Stream logs to monitoring tools for real-time issue detection, such as failed requests or slow responses.
Error Tracking and Debugging
Detailed structured logs make debugging faster and more accurate.
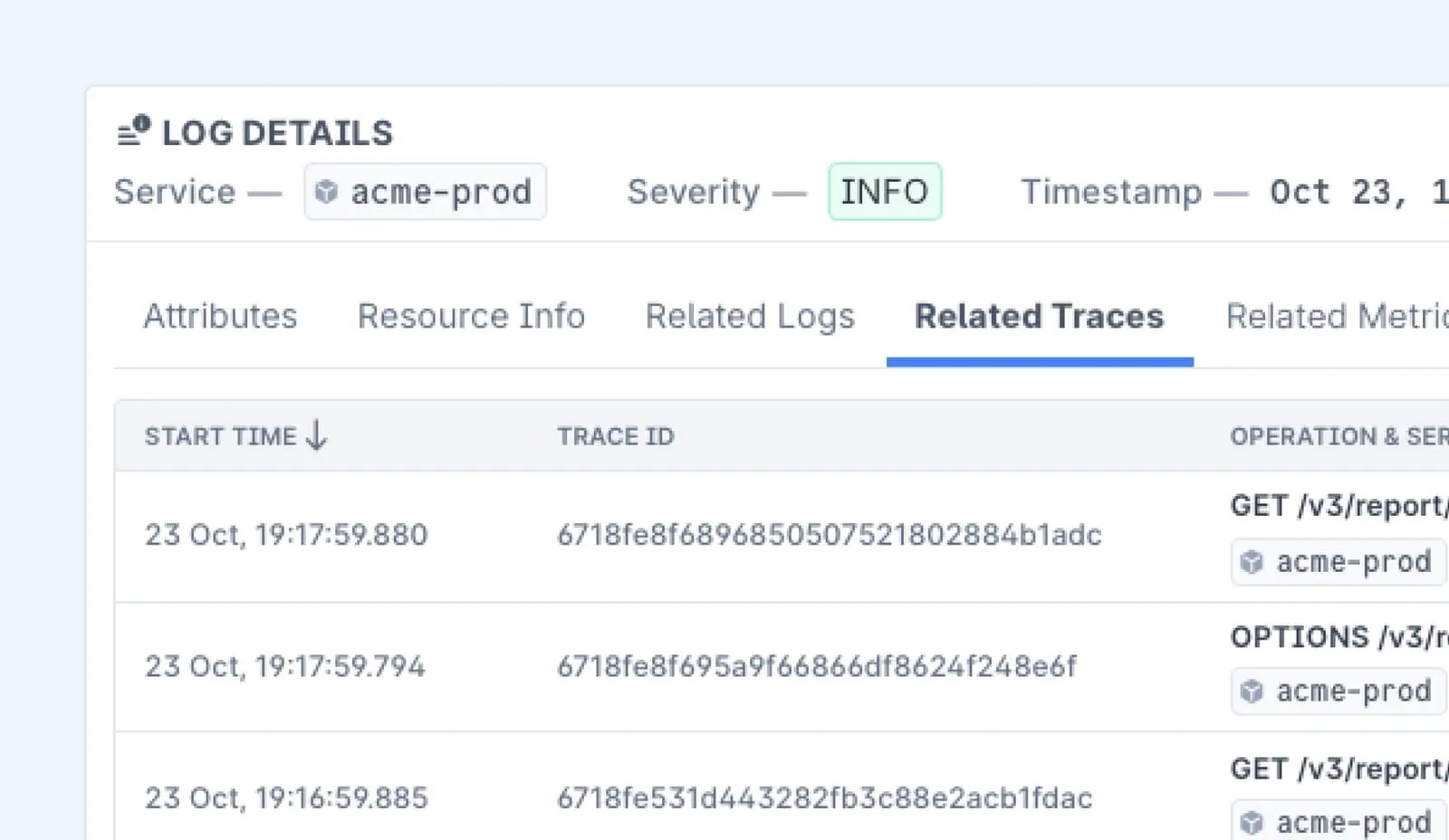
Practical Error Handling and Exception Tracking
Capture exceptions with structured context, including full traceback information:
import structlog
class ErrorLogger:
def __init__(self):
self.logger = structlog.get_logger()
def capture_exception(self, error, context=None):
error_context = {
"error_type": error.__class__.__name__,
"error_message": str(error),
"module": error.__module__,
**(context or {})
}
self.logger.error("exception_occurred", exc_info=True, **error_context)Integration with Modern Observability Platforms
ELK Stack Integration
Configure Structlog to work with the ELK stack:
import structlog
structlog.configure(
processors=[
structlog.processors.TimeStamper(fmt="iso"),
structlog.processors.format_exc_info,
structlog.processors.JSONRenderer(),
]
)OpenTelemetry Integration
Add trace context (trace_id, span_id) to logs:
from opentelemetry import trace
def add_trace_info(_, __, event_dict):
span = trace.get_current_span()
if span:
context = span.get_span_context()
event_dict["trace_id"] = hex(context.trace_id)
event_dict["span_id"] = hex(context.span_id)
return event_dict
structlog.configure(processors=[add_trace_info])
Performance Optimization Techniques
Buffered Logging
Batch log entries to improve throughput:
from queue import Queue
from threading import Thread
class BufferedLogger:
def __init__(self, buffer_size=1000):
self.buffer = Queue(maxsize=buffer_size)
self.worker = Thread(target=self._process_buffer, daemon=True)
self.worker.start()
def _process_buffer(self):
while True:
logs = [self.buffer.get()]
while not self.buffer.empty() and len(logs) < 100:
logs.append(self.buffer.get_nowait())
for log in logs:
print(log) # Replace with actual log handlingTesting and Mocking
Capture and test logs using pytest:
import structlog
import pytest
class LogCapture:
def __init__(self):
self.entries = []
def __call__(self, logger, method_name, event_dict):
self.entries.append(event_dict)
return event_dict
@pytest.fixture
def captured_logs():
capture = LogCapture()
structlog.configure(processors=[capture])
return capture.entriesSchema Evolution and Backward Compatibility
Define versioned log schemas to ensure compatibility:
from typing import TypedDict
class BaseLogSchema(TypedDict):
timestamp: str
version: str
event_type: str
class UserLogSchema(BaseLogSchema):
user_id: str
action: str
def create_log_entry(schema):
base_entry = {"timestamp": "2024-12-10T00:00:00", "version": "1.0", "event_type": "user_action"}
return {**base_entry, **schema}Conclusion
Logging is more than just messages—it’s about understanding your system. With structlog, you can enhance logs to be actionable and insightful, whether working on a monolith or a microservices architecture.
Start using structlog to build smarter, more organized logs today!
FAQs
1. What is the main advantage of using structlog over traditional logging?
Structlog allows you to create structured logs with key-value pairs, making them easier to analyze and more informative compared to plain text logs. It improves readability, debugging, and integration with modern observability tools.
2. Can structlog work with existing Python logging frameworks?
Yes, structlog integrates easily with Python’s built-in logging module and other libraries like loguru. This allows you to enhance your current logging setup without a complete overhaul.
3. How does structlog handle performance in high-throughput systems?
Structlog supports features like asynchronous and buffered logging to minimize performance overhead. Its efficient processing pipelines ensure that logging does not become a bottleneck.
4. What tools does structlog integrate with for monitoring and observability?
Structlog integrates with observability platforms like OpenTelemetry, Datadog, and the ELK stack. It can enrich logs with trace IDs, timestamps, and other metadata for better correlation and monitoring.
5. Can I customize how my logs are formatted with structlog?
Absolutely! Structlog provides customizable pipelines for log formatting, processing, and rendering. You can choose between JSON, plain text, or any other format that fits your needs.
6. Is structlog suitable for microservices architectures?
Yes, structlog is excellent for microservices. It allows you to attach unique request IDs or other metadata, enabling easier correlation of logs across services.
7. How does structlog handle context preservation?
Structlog enables context preservation by binding metadata (e.g., user IDs, session IDs) to a logger. This metadata gets included in all log entries, making it easier to trace events and debug issues.
8. What are processors in structlog, and why are they important?
Processors are functions that modify log entries before they’re recorded. They can add timestamps, redact sensitive information, or enrich logs with additional context.
9. Can structlog help with exception tracking?
Yes, structlog can capture exceptions with full traceback information. You can log detailed error context, such as error type, module, and additional metadata, to improve debugging.
10. Is structlog compatible with Python’s async features?
Yes, structlog supports asynchronous logging, which is particularly useful for high-concurrency systems, ensuring that logs are written without blocking application logic.
11. Can structlog help with schema evolution in logs?
Yes, structlog supports managing schema changes by defining versioned log schemas. This ensures backward compatibility and smooth handling of logs as your system evolves.
12. How do I test and validate logs in a Python project using structlog?
You can capture and test logs using libraries like pytest by configuring structlog with custom processors, such as a log capture function, to validate log outputs during tests.









